Consider the following:
Light: South or southeast facing, avoid obstructions
Drainage: Slightly elevated to prevent waterlogging
Wind direction: Avoid strong winds or install windbreaks
Soil: Fertile, loose soil suitable for the target crop




Consider the following:
Light: South or southeast facing, avoid obstructions
Drainage: Slightly elevated to prevent waterlogging
Wind direction: Avoid strong winds or install windbreaks
Soil: Fertile, loose soil suitable for the target crop
Common hydro farming equipment includes:
Temperature control system (heater, fan, shade net)
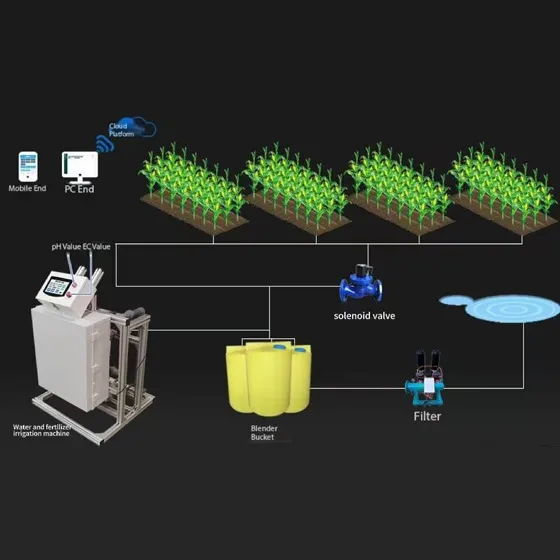
Irrigation system (drip irrigation, sprinkler irrigation, integrated water and fertilizer)
Lighting system (LED plant lights, suitable for areas with low light levels)
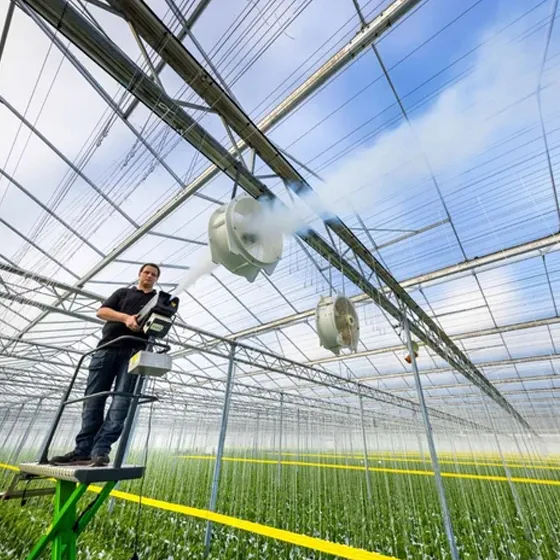
Ventilation system (side windows, skylights, exhaust fans)
Monitoring system (temperature and humidity sensors, CO₂ monitor)
Winter insulation: heaters, floor heating, thermal blankets
Summer cooling: sunshade nets, wet curtains, fans, ventilation
Smart temperature control: constant temperature system (automatic adjustment with set thresholds)
Structural inspection: Regularly reinforce the frame and repair damaged film.
Equipment maintenance: Clean sensors and inspect the irrigation system.
Disinfection: Disinfect the soil and equipment at the end of each season.
Increase ventilation,Use anti-drip film,Install dehumidification equipment
Windproof: Reinforce the frame and use film tape.
Snowproof: Clear snow promptly or choose a pressure-resistant structure.
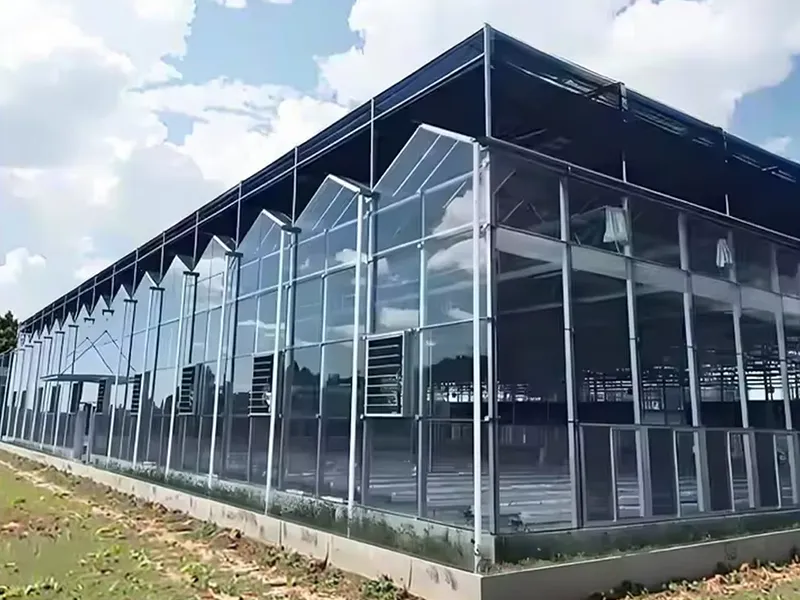
A greenhouse is an artificially controlled growing environment, typically covered by a light-transmitting material (such as glass or plastic film) and equipped with temperature control, lighting, ventilation, and other equipment to regulate the internal climate and enable off-season or high-yield cultivation.
Common types include:
Plastic greenhouses (economical, suitable for short-term crops)
Glass greenhouses (excellent light transmission, durable, suitable for long-term cultivation)
Solar greenhouses (utilize natural light, energy-saving, suitable for northern regions)
Smart greenhouses (automated control, suitable for precision agriculture)
Dehumidification: ventilation, dehumidifiers
Reasonable irrigation: avoid overwatering and use drip irrigation to reduce leaf wetness
Monitoring: use humidity sensors to maintain 60%-80% relative humidity (depending on the crop)
Scientific crop rotation: Avoid continuous cropping
Precision fertilization: Integrated water and fertilizer application to supplement nutrients as needed
Supplemental lighting: Use LED lighting on rainy days
Pest and disease control: Insect screens, biological control, and regular disinfection
Small home greenhouse: 3-6 meters wide, 5-10 meters long, 2-3 meters high Commercial greenhouse: 8-12 meters wide, 30-100 meters long, 4-6 meters high (to facilitate mechanical operation)
Specialty crops (such as vines) require more space.
Through Environmental controllers (automatically adjust temperature, humidity, and light)
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors (real-time data monitoring and remote control)
Automatic irrigation systems (timed or on-demand watering and fertilization)
Vegetables: Tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, leafy vegetables
Flowers: Roses, lilies, succulents
Fruits: Strawberries, watermelons, grapes (requires a taller greenhouse)
Seedlings: Start seedlings early to extend the growing season


